Home » CBSE Guide » Class 10 » Science » Ch-1 Revision Notes
Chapter 1 - Chemical Reactions and Equations
Revision Notes
A chemical reaction involves a chemical change in which the molecules of one substance break apart and join together with those of another substance to create a different compound having entirely new properties.
- The atoms and molecules which take part in a chemical reaction are called reactants.
- The new substances (the atoms and molecules) produced as a result of chemical reaction are called products.
- In a chemical reaction, reactants are converted into products. No new atoms are created, and no atoms are destroyed. In other words, only rearrangement of atoms takes place in a chemical reaction.
For example:
Hydrogen gas (H2) can react (burn) with oxygen gas (O2) to form water (H2O). The chemical equation for this reaction is written as:

Here, 2 molecules of hydrogen gas combine with one molecule of oxygen gas to form two molecules of water.
Physical change: Physical change is a process in which the substance experiences change in its physical properties like shape, colour, size, appearance, state (i.e. solid, liquid, gas), etc., without making any change in their chemical composition. Eg., melting of ice into water, dissolving sugar in water.
Chemical change: Chemical change is defined as the process in which the atoms of one or more substances are broken or combined to form a new substance. Eg., Rusting of iron, fermenting of milk into curd.
DETERMINATION OF A CHEMICAL REACTION:
The conversion of reactants into products in a chemical reaction is often accompanied by some features which can be easily observed. Characteristics of a chemical reaction:
- Evolution of a gas
- Formation of a precipitate
- Change in colour
- Change in temperature
- Change in state
- New substances are formed
Precipitate: A precipitate is a solid insoluble product which separates out from the solution during a chemical reaction. E.g., When an aqueous solution of lead nitrate Pb(NO3)2 is added to an aqueous solution of potassium iodide (KI), a yellow precipitate of lead iodide (PbI2) is formed along with some colorless potassium nitrate KNO3 (which stays in solution):

Based on energy differences between reactants and products the chemical reactions are classified into two types. They are exothermic reaction and endothermic reaction:
- An exothermic process releases heat and causes the temperature of the immediate surroundings to rise. E.g., rusting iron, chemical reaction between quicklime and water to form slaked lime is characterized by release of heat energy.
- An endothermic process absorbs heat and cools the surroundings. E.g., producing sugar by photosynthesis, formation of nitric oxide from nitrogen and oxygen.
CHEMICAL EQUATIONS
- A chemical equation is a symbolic representation of the reactants and the products using their chemical formulae. Chemical equations are a way of describing a chemical reaction.
Features of a chemical equation:
For example,

Here, A and B are the reactants and C and D are the products.
- The reactants are written on the left side of the arrow and the products are written on the right side.
- The arrow shows the direction of the reaction (the direction of change from reactants to products).
- The optimum conditions that are required for the reaction to take place are generally written above or below the arrow mark.
- The number of atoms of each element involved in the reaction should remain constant.
- The number of molecules of each chemical is represented by a numerical coefficient, which is always a whole number.
- An arrow pointing downward indicates that the product is a precipitate (↓) and an arrow pointing upward shows that one of the products is a gaseous one (↑).
- The physical state of the chemicals may be written near the formula by using short forms such as (s) ------ solid ; (l) ------ liquid ; (g) ------ gas or vapor and (aq. ) ------ aqueous solution.
There are two types of chemical equations namely word equation and symbol equation
- Word equations are a way of explaining chemical reactions using the names of substances involved. No symbols or numbers are used in word equations.
- Symbol equation uses the chemical formulae of the reactants and products with their elemental symbols to represent them in a chemical reaction.
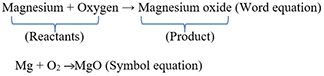
A simple example of a chemical reaction is when a magnesium ribbon is burnt in oxygen; it gets converted to magnesium oxide
Here is the equation in both words and symbols:
« Back to Menu | Page 1 | Page 2 | Page 3

