Home » CBSE Guide » Class 10 » Science » Ch-1 Revision Notes
Chapter 1 - Chemical Reactions and Equations
Revision Notes
Page 3 of 3
Double Displacement Reaction
- A chemical reaction in which two atoms or a group of atoms (ions) are exchanged between the reactants to form new compounds are called double displacement reactions.
- General formula for double displacement reaction: XY + ZA → XZ + YA
- Example:
When barium chloride solution is added to sodium sulphate solution, then a white precipitate of barium sulphate is formed along with sodium chloride solution.
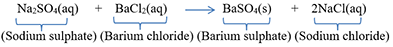
-An exchange of ions takes place in this reaction.
-In this reaction, barium sulphate is formed as a white, insoluble solid called precipitate which separates out suddenly from the solution.
- Any reaction in which an insoluble solid called precipitate is formed that separates from the solution is called a precipitation reaction.
- General formula for precipitation reaction:
A + soluble salt B → precipitate + Soluble salt C
Oxidation and Reduction reactions:
- Oxidation is a chemical process in which a substance gains oxygen or loses hydrogen.
- If a substance gains oxygen or loses hydrogen during a reaction, it is said to be oxidized
- The substance which gives gains oxygen or loses hydrogen during a reaction, the substance is called the oxidizing agent.
- An oxidizing agent gets reduced
- Example:
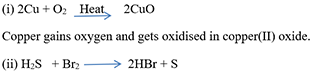
- Reduction is a chemical process in which a substance gains hydrogen or loses oxygen.
-If a substance gains hydrogen or loses oxygen during a reaction, it is said to be reduced.
- The substance (reactant) which is responsible for removing oxygen or gaining hydrogen for reduction during a reaction is called the reducing agent.
- A reducing agent gets oxidised.
- Examples:
(i) CuO + H2 → Cu + H2O
Copper loses oxygen and gets reduced
(ii)H2S + Cl2 → 2 HCl+ S
Sulphur loses hydrogen and gets reduced.
- Redox reaction: When oxidation and reduction takes place simultaneously in a reaction, it is known as redox reaction.
- Example:
ZnO + C → Zn + CO
Here, ZnO loses oxygen and gets reduced to Zn. Similarly, carbon gains oxygen and gets oxidized to CO
- Effect of oxidation reactions in everyday life:
Oxidation has damaging effect on metals as well as on food. There are two common effects of oxidation reactions which we observe in daily. These are:
- Corrosion of metals:
When a metal is attacked by substances around it such as moisture, acids, etc., it is said to corrode and this process is called corrosion.
- The black coating on silver and the green coating on copper are other examples of corrosion.
Prevention:
- By galvanization
- By painting metal surfaces
- By regularly oiling or greasing the metal surfaces.
Galvanisation: Coating a thin layer of Zinc on metal surfaces by electroplating.
- Rancidity: When fats and oils are oxidised, they become rancid and their smell and taste change.
Prevention:
- Antioxidants are added to foods containing fats and oils.
- Keeping food in air tight containers help to slow down oxidation.
- By removing oxygen gas and filling nitrogen gas at the time of packing the food.
- Rancidity can be retarded to a certain extent by storing food away from heat and light.
- By keeping food in the refrigerator which will eventually slow down oxidation.
« Back to Menu | Page 1 | Page 2 | Page 3

