Home » CBSE Guide » Class 10 » Science » Ch-1 Exemplar Questions and Solutions
Chapter 1 - Chemical Reactions and Equations
Exemplar Questions and Solutions
Short Answer Questions
1) Write the balanced chemical equations for the following reactions and identify the type of reaction in each case.
(a) Nitrogen gas is treated with hydrogen gas in the presence of a catalyst at 773K to form ammonia gas.

This is a combination reaction as two or more elements are combing to form a compound.
(b) Sodium hydroxide solution is treated with acetic acid to form sodium acetate and water.

It is a balanced equation and is a double displacement reaction as two compounds (Sodium hydroxide and acetic acid) react by exchange of ions to form two new compounds.
(c) Ethanol is warmed with ethanoic acid to form ethyl acetate in the presence of concentrated H2SO4.
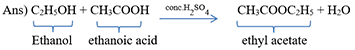
It is already a balanced equation as the number of various atoms is equal on both sides. This reaction is a combination reaction as two or more elements are combing to form a compound.
(d) Ethene is burnt in the presence of oxygen to form carbon dioxide, water and releases heat and light.
Ans) C2H4 + 3O2 → 2CO2 + 2H2O
It is a redox reaction as there is a change in the oxidation number of carbon and oxygen. Carbon is oxidized as it gains oxygen and C2H4 is the reducing agent while oxygen is reduced, as it loses oxygen and the oxidizing agent is O2
2) Write the balanced chemical equations for the following reactions and identify the type of reaction in each case.
(a) Thermit reaction, iron (III) oxide reacts with aluminium and gives molten iron and aluminium oxide.
Ans) Fe2O3 + 2Al → 2Fe + Al2O3 + Heat + Light
It is an exothermic redox reaction. As an incredible amount of heat is produced, it is an exothermic reaction. As aluminium is more reactive than iron, it displaces iron from ferric oxide (Fe2O3). The aluminium gains oxygen from ferric oxide and therefore, aluminium gets oxidized while iron is reduced as it loses oxygen during the redox reaction.
(b) Magnesium ribbon is burnt in an atmosphere of nitrogen gas to form solid magnesium nitride.
Ans) 3MgS + N2 → 2Mg3N2
The above reaction is a combination reaction as two or more elements are combing to form a compound
(c) Chlorine gas is passed in an aqueous potassium iodide solution to form potassium chloride solution and solid iodine.
Ans) 2KI + Cl2 → 2KCl + I2
The above reaction is a displacement reaction because chlorine being smaller than Iodine, it is more reactive than Iodine. Therefore, it displaces iodine from potassium iodide and forms potassium chloride.
(d) Ethanol is burnt in air to form carbon dioxide, water and releases heat.
Ans) C2H5OH + 3O2 → 2CO2 + 3H2O + Heat
It is a redox reaction as there is a change in the oxidation number of carbon and oxygen. Carbon is oxidized as it gains oxygen and C2H5OH is the reducing agent while oxygen is reduced, as it loses oxygen and the oxidizing agent is O2. It is an exothermic reaction as there is release of heat energy.
3) Complete the missing components/variables given as given as x and y in the following reactions
a) Pb(NO3)2 (aq) + 2KI (aq) → PbI2 (x) +2KNO3 (y)
Ans) Pb(NO3)2 (aq) + 2KI (aq) → PbI2 (s) + 2KNO3 (aq)
b) Cu (s) + 2AgNO3 (aq) → Cu(NO3)2 + X (s)
Ans) Cu (s) + 2AgNO3 (aq) → Cu(NO3)2 + Ag (s)
c) Zn (s) + H2SO4 (aq) → ZnSO4 (x) + H2 (y)
Ans) Zn (s) + H2SO4 (aq) → ZnSO4 (aq) + H2 (g)
4) Which among the following changes are exothermic or endothermic in nature?
a) Decomposition of ferrous sulphate
b) Dilution of sulphuric acid
c) Dissolution of sodium hydroxide in water
d) Dissolution of ammonium chloride in water
Ans) (b) and (c) are exothermic as heat is released in these changes.
(a) and (d) are endothermic as heat is absorbed in these change
5) Identify the reducing agent in the following reactions:
a) 4NH3 + 5O2 → 4NO + 6H2O
Ans) In this reaction, nitrogen of ammonia gains oxygen to form NO. It means that NH3 is oxidized. So, it acts as a reducing agent in the above given reaction. Therefore, substance oxidized is NH3 and thus it is the reducing agent while the substance reduced is O2 and therefore, the oxidizing agent- is O2.
b) H2O + F2 → HF + HOF
Ans) H2O is oxidized to HOF by losing hydrogen atom. Hence, H2O is the reducing agent. F2 is reduced to HF by gaining hydrogen atom. Hence, F2 is the oxidizing agent.
c) Fe2O3 + 3CO → 2Fe + 3CO2
Ans) In this reaction, oxygen is removed from Fe2O3 and is added to CO. So, Fe2O3 is reduced to Fe and CO is oxidized to CO2. Fe2O3 is the oxidizing agent and CO is the reducing agent.
d) 2H2 + O2 → 2H2O
Ans) In this reaction, 2H2 gains oxygen (while reacting with O2) and becomes 2H2O. So, here 2H2 gets oxidized and therefore, 2H2 is the reducing agent.
« Back to Menu | Page 1 | Page 2 | Page 3 | Page 4

