Home » CBSE Guide » Class 10 » Science » Ch-1 Exemplar Questions and Solutions
Chapter 1 - Chemical Reactions and Equations
Exemplar Questions and Solutions
Short Answer Questions
Page 3 of 4
12) Which among the following are physical or chemical changes?
(a) Evaporation of petrol
Ans) Physical change. Petrol kept in the sun evaporates. When the petrol vapours are collected, the vapours change to liquid petrol.
(b) Burning of Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG)
Ans) Burning of LPG involves both physical and chemical changes. Burning of LPG in our kitchen is another such example in which a physical change occurs when LPG come out of cylinder and is converted from liquid to gaseous state and a chemical change occurs when this gas burn in air.
(c) Heating of an iron rod to red hot
Ans) Physical change. If you heat an iron bar until it glows red hot, it is still chemically the same iron.
(d) Curdling of milk
Ans) Chemical change. Curd is produced from milk. The curd formed is a new substance having entirely different chemical properties. It is irreversible, as milk cannot be got back from curd. Hence, setting of curd is a chemical change.
(e) Sublimation of solid ammonium chloride
Ans) Sublimation of solid ammonium chloride involves both physical and chemical changes Physical change. Sublimation is the process of change of state from solid directly into gaseous state. On heating, solid ammonium chloride changes directly to vapour state. On cooling, the vapours form solid ammonium chloride again.
Chemical change. On heating strongly above 340oC, the white solid ammonium chloride, thermally decomposes into a mixture of two colourless gases ammonia and hydrogen chloride.
The products ammonia and chlorine recombine to form ammonium chloride. This is also a chemical change. It is also a reversible reaction.

13) During the reaction of some metals with dilute hydrochloric acid, following observations were made. Explain these observations giving suitable reasons.
(a) Silver metal does not show any change
Ans) No change takes place because silver being a noble metal does not react with hydrochloric acid under normal situations. Metals like copper, silver, gold and platinum are placed below hydrogen in the reactivity series and hence will not react with dilute acid. They cannot displace hydrogen from acids.
Ag(s) + HCl(aq) → No reaction
(b) The temperature of the reaction mixture rises when aluminium (Al) is added.
Ans) When aluminium is added to dilute HCl, it displaces hydrogen from the acid as it is more reactive than hydrogen and forms aluminium chloride and hydrogen gas. The reaction of Al with dil. HCl is exothermic, i.e. heat is released in the reaction thereby increasing the temperature of the reaction mixture.

(c) The reaction of sodium metal is found to be highly explosive.
Ans) The reaction of sodium metal is found to be highly explosive because it is an exothermic reaction. Sodium being very reactive metal, reacts vigorously with dil HCl the evolution of heat too.
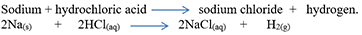
(d) Some bubbles of a gas are seen when lead (Pb) is reacted with the acid.
Ans) Lead reacts very slowly with dilute hydrochloric acid as it is placed just above hydrogen in the reactivity series. Lead displaces the H from HCl and there is the evolution of colourless bubbles of a gas. The bubbles formed when lead reacts with dilute Hcl shows that a gas is being made. The gas is hydrogen.
Pb(s) + 2HCl (aq) → PbCl2(s) + H2(g)
14) A substance X, which is an oxide of a group 2 element, is used intensively in the cement industry. This element is present in bones also. On treatment with water it forms a solution which turns red litmus blue. Identify X and also write the chemical reactions involved.
Ans) Element ‘X’ is calcium. When calcium oxide reacts with water it forms calcium hydroxide (slaked lime). Since calcium hydroxide is a base, thus it turns red litmus blue.

Calcium belongs to group 2 of the periodic table. It is used in cement industry and is also found in bones.
15) Write a balanced chemical equation for each of the following reactions and also classify them.
(a) Lead acetate solution is treated with dilute hydrochloric acid to form lead chloride and acetic acid solution.
Ans) Pb(CH3COO)2 + 2HCl → PbCl2 + CH3COOH
It is a double displacement reaction as two compounds (Lead acetate and hydrochloric acid) react by exchange of ions to form two new compounds.
(b) A piece of sodium metal is added to absolute ethanol to form sodium ethoxide and hydrogen gas.
Ans) 2Na + 2C2H5OH → 2C2H5ONa + H2
It is a displacement reaction sodium metal displaces the hydrogen in the –OH group to form sodium ethoxide and hydrogen gas.
(c) Iron (III) oxide on heating with carbon monoxide gas reacts to form solid iron and liberates carbon dioxide gas.
Ans) Fe2O3 + 3CO → 2Fe + 3CO2
It is a redox reaction as each carbon atom increases its oxidation number from +2 to +4, so each carbon atom in CO(g) is oxidized, and CO(g) is the reducing agent. Each iron atom in Fe2O3 decreases its oxidation number from +3 to 0, so each Fe atom in Fe2O3 is reduced and Fe2O3 is the oxidizing agent
(d) Hydrogen sulphide gas reacts with oxygen gas to form solid sulphur and liquid water
Ans) 2H2S + O2 → 2S + 2H2O
The above given chemical reaction is a redox reaction. S atoms in H2S are oxidized, O atoms in O2 are reduced, O2 is the oxidizing agent, and H2S is the reducing agent.
« Back to Menu | Page 1 | Page 2 | Page 3 | Page 4

