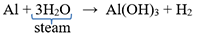Home » CBSE Guide » Class 10 » Science » Ch-1 Exemplar Questions and Solutions
Chapter 1 - Chemical Reactions and Equations
Exemplar Questions and Solutions
Long Answer Questions
1) On heating blue coloured powder of copper (II) nitrate in a boiling tube, copper oxide (black), oxygen gas and a brown gas X is formed
a) Write a balanced chemical equation of the reaction.

b) Identify the brown gas X evolved.
Ans) The brown gas 'X' is nitrogen dioxide (NO2)
c) Identify the type of reaction.
Ans) The above reaction is a thermal decomposition reaction as decomposition of copper nitrate takes place due to heating.
d) What could be the pH range of aqueous solution of the gas X?
Ans) Nitrogen dioxide dissolves in water to form an acidic solution as oxides of non-metals are acidic. Hence, an aqueous solution of this gas would be acidic with a pH of less than 7.
2) Give the characteristic tests for the following gases:
a) CO2
Ans) The specific characteristic test for CO2 is to bubble the test gas through limewater(calcium hydroxide) solution. When carbon dioxide is bubbled through limewater, a solid precipitate of
calcium carbonate(limestone) is formed and this makes the lime water milky.
Calcium hydroxide + carbon dioxide → calcium carbonate + water.
Ca(OH)2(aq) + CO2(g) → CaCO3(s) + H2O(l)
Carbon dioxide turns lime water milky as it forms calcium carbonate with lime water. This is the characteristics test for carbon dioxide.
b) SO2
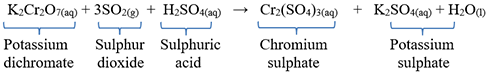
Ans) Sulphur dioxide gas turns moist litmus paper from blue to red. Sulphur dioxide gas will put out a lit splint. But, the specific test for SO2 is that it turns acidified potassium dichromate(VI) solution from orange to green.
c) O2
Ans) When a glowing wooden splint is introduced into in a test tube containing a sample of the gas. The glowing splint re-ignites to a flame if the sample of gas is oxygen. This is the characteristic test for oxygen gas.
d) H2
Ans) When we introduce the light of a wooden splint, but do not blow out the flame into the mouth of the test tube containing a sample of the gas. If the gas is hydrogen, you will hear a slight explosive "pop" sound. When a burnt candle or match stick, is introduced into in a test tube of hydrogen, it burns with pop sound, which is the characteristic test for hydrogen gas.
2H2(g) + O2(g) → 2H2O(l) + energy
3) What happens when a piece of
a) Zinc metal is added to copper sulphate solution?
Ans) Zinc being more reactive than copper displaces copper from its solution and a solution of zinc sulphate and copper is formed. This reaction is an example of displacement reaction as Zn displaces Cu from CuSO4 to form ZnSO4
Zn(s) + CuSO4(aq) → Cu(s) + ZnSO4(aq)
b) Aluminium metal is added to dilute hydrochloric acid?
Ans) When aluminium metal is added to dilute HCl, it displaces hydrogen from the acid and forms aluminium chloride and hydrogen gas as Aluminium is more reactive than hydrogen.
2Al(s) + 6HCl(aq) → 2AlCl3(aq) + 3H2(g)
c) Silver metal is added to copper sulphate solution? Also, write the balanced chemical equation if the reaction occurs
Ans) When silver metal is added to copper sulphate solution, no reaction takes place because silver is less reactive than copper cannot displace copper from its salt solution.
Ag (s) + CuSO4(aq) → No reaction
4) What happens when zinc granules are treated with dilute solution of H2SO4, HCl, HNO3, NaCl and NaOH, also write the chemical equations if reaction occurs.
Ans) The reaction of Zn granules with
(a) Dilute H2SO4
Zn(s) + H2SO4(aq) → ZnSO4(aq) + H2(g)
Zinc being more reactive than hydrogen displaces hydrogen from dilute acids(dil Sulphuric acid). It reacts with dilute sulphuric acid to form zinc sulphate and hydrogen gas is evolved. This is a displacement reaction of a non-metal by a metal.
(b) Dilute HCl
Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) → ZnCl2(aq) + H2(g)
Zinc being more reactive than hydrogen displaces hydrogen from dilute acids(dil hydrochloric acid). It reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid to form zinc chloride and hydrogen gas is evolved. This is a displacement reaction
(c) Dilute HNO3
Zinc reacts with dilute nitric acid to give zinc nitrate and hydrogen gas.
Zn(s) + 2HNO3(aq) → Zn(NO3)2(aq) + H2(g)
(d) NaCl solution
Zn(s) + NaCl (aq) → No reaction
As Zinc is less reactive than sodium, no reaction takes place between them
(e) NaOH solution
Zinc reacts with sodium hydroxide to produce zincate sodium and hydrogen. Heat (near 550°C) is required to catalyse the reaction.
Sodium Zincate is only formed only if NaOH is provided in excess.
Zn+2NaOH → Zn(OH)2+2Na
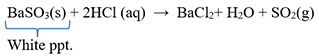
5) On adding a drop of barium chloride solution to an aqueous solution of sodium sulphite, white precipitate is obtained.
(a) Write a balanced chemical equation of the reaction involved
Ans) BaCl2 + Na2SO3 → BaSO3 + 2NaCl
(b) What other name can be given to this precipitation reaction?
Ans) The other name that can be given to this precipitation reaction is double displacement reaction.
(c) On adding dilute hydrochloric acid to the reaction mixture, white precipitate disappears. Why?
Ans) Barium chloride reacts with sodium sulphite and forms barium sulphite(white precipitate). When dilute hydrochloric acid is added to Barium Sulphite(BaSO3), it decomposes to produce Barium chloride, sulphur dioxide gas and water.
BaSO3(s) + 2HCl (aq) → BaCl2+ H2O + SO2(g)
White ppt.
As BaCl2 is a soluble substance, hence the white precipitate of barium sulphite disappears.
6) You are provided with two containers made up of copper and aluminium. You are also provided with solutions of dilute HCl, dilute HNO3, ZnCl2 and H2O. In which of the above containers these solutions can be kept?
Ans) (A) When solutions are kept in copper container
(a) Dilute HCl
The metal copper is less reactive than hydrogen and they do not replace hydrogen from water or acid. Copper does not react with dilute HCl. Therefore, it can be kept.
(b) Dilute HNO3
Nitric acid is an oxidizing acid that will dissolve most metals to form soluble metal nitrates. Thus, Copper is oxidized by dilute nitric acid, HNO3, while the nitric acid gets reduced to nitrogen dioxide. If we are using concentrated nitric acid, HNO3, and in excess then the ratio is 1:4 copper to nitric acid. If we are using dilute nitric acid, HNO3, then the ratio is 3:8 copper to nitric acid.
4 HNO3(conc) + Cu(s) → Cu(NO3)2(s and aq) + 2 NO2(g) + 2 H2O(l)
3Cu+8HNO3(dil) → 3Cu(NO3)2+2NO + 4H2O
(c) ZnCl2
Zinc is more reactive than copper (Cu) therefore, no reaction takes place. Hence, ZnCl2 can be kept in copper vessels.
Cu(s) + ZnCl2 (aq) → no reaction
(c) H2O
Copper does not react with water. Therefore, water can be kept in copper vessels.
(B) When solutions are kept in aluminium containers
(a) Dilute HCl
Aluminium reacts with dilute HCl to form hydrogen gas and aqueous aluminum chloride. Therefore, dil HCl cannot be kept in aluminium containers.
2 Al(s) + 6HCl(aq) → 2 AlCl3(aq) + 3 H2(g)
(b) Dilute HNO3
When dil HNO3 is placed in aluminium containers, a thin protective oxide layer is formed around the metal surface as HNO3 is an oxidising agent. This thin protective oxide layer does-not react with HNO3 and henceforth prevents further reaction. Therefore, dil HNO3 can be stored in aluminium containers.
(c) ZnCl2
Aluminium being more reactive than zinc can displace zinc ion from the solution. Therefore, ZnCl2 cannot be kept in aluminium containers.
2 Al + 3 ZnCl2 → 2 AlCl3 + 3Zn
(d) H2O
Aluminium does not react with either cold or hot water. Therefore, water can be kept in aluminium containers.
But, aluminium can displace hydrogen from steam to form aluminium hydroxide and hydrogen gas